• Recommended application for Glass Media.
Application Type | Removed by use of Glass Media | |
Drinking water | Iron, Manganese, Arsenate and | |
some priority chemicals | ||
Municipal Wastewater | Phosphorous & Bacteria, BOD, | |
COD & TOC |
Recommended Glass Media arrangement from top to bottom (on a bottom plate), in Pressure Filters:
Activated Glass Filtration Media replaces traditional sand media in all filtration applications. It is manufactured from a specific glass type and processed to obtain the optimum particle size and shape, and then activated to increase the surface area by 300 times over crushed glass or sand. The high surface area is negatively charged (zeta potential) to electro-statically attract organics and small particles. It also has permanent metal oxide catalysts, creating a high redox potential, to make AGFM self-sterilizing.
Main Benefits:
- Over 30% lower running costs sand
- Over 50% lower chlorine consumption and lower disinfection by- products sand
- Filtration down to several microns at 100% efficiency without filtration aids
- More than 4 times longer lifecycle than sand
- Specifically engineered product, targeted for an efficient removal of priority metal oxides and other target constitutes
Guaranteed prevention of channeling & biological fouling on the AGFM surface
Grade | Size (mm) | Comm-ercial | High | Ultra |
Purifi-cation | Purifi-cation | Purifi-cation | ||
Grade 0 | 0.25 – 0.50 | N/A | 20% | 60% |
Grade 1 | 0.4 – 1.0 | 70% | 50% | 20% |
Grade 2 | 1 – 2 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
Grade 3 | 2 – 6 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
Recommended Glass Media arrangement from top to bottom (on a bottom plate), in Pressure Filters:
Activated Glass Filtration Media replaces traditional sand media in all filtration applications. It is manufactured from a specific glass type and processed to obtain the optimum particle size and shape, and then activated to increase the surface area by 300 times over crushed glass or sand. The high surface area is negatively charged (zeta potential) to electro-statically attract organics and small particles. It also has permanent metal oxide catalysts, creating a high redox potential, to make AGFM self-sterilizing.
Main Benefits:
- Over 30% lower running costs sand
- Over 50% lower chlorine consumption and lower disinfection by- products sand
- Filtration down to several microns at 100% efficiency without filtration aids
- More than 4 times longer lifecycle than sand
- Specifically engineered product, targeted for an efficient removal of priority metal oxides and other target constitutes
Guaranteed prevention of channeling & biological fouling on the AGFM surface
Grade | Size (mm) | Comm-ercial | High | Ultra |
Purifi-cation | Purifi-cation | Purifi-cation | ||
Grade 0 | 0.25 – 0.50 | N/A | 20% | 60% |
Grade 1 | 0.4 – 1.0 | 70% | 50% | 20% |
Grade 2 | 1 – 2 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
Grade 3 | 2 – 6 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
Products
Water treatment plants engage in several activities to ensure the purification of water for various purposes. Some key activities and components involved include:
- DM Plants (Demineralization Plants): DM plants are designed to remove minerals and salts from water, producing demineralized or deionized water. These plants typically use ion exchange resins to replace ions in the water with hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, resulting in highly purified water.
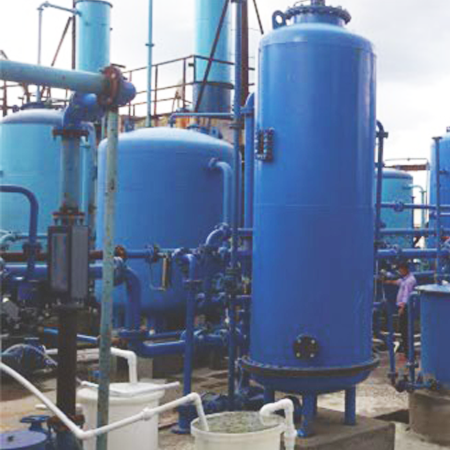
- Carbon Filter: Carbon filters are employed to eliminate impurities, chemicals, and contaminants from water. Activated carbon, with its large surface area and adsorptive properties, is effective in trapping and removing organic substances, chlorine, and other pollutants.
- Sand Filter: Sand filters are a common method for removing suspended solids and particles from water. Water passes through a bed of sand, where solids are trapped, allowing cleaner water to pass through. Sand filters are effective in various applications, including wastewater treatment and swimming pool filtration.
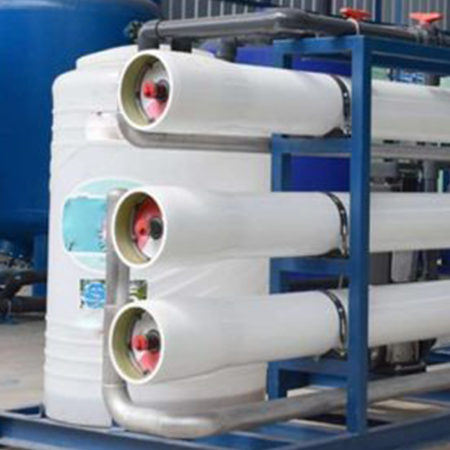
- Industrial RO (Reverse Osmosis): Industrial RO systems use a semi-permeable membrane to remove a wide range of impurities, including dissolved salts, minerals, and contaminants, from water. This process is widely used for producing high-quality, purified water in industrial settings.
These water treatment activities collectively contribute to enhancing water quality, making it suitable for specific applications such as drinking water, industrial processes, and more. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall treatment process, ensuring that water meets the required standards for its intended use.